- Genetically Modified Organisms
- Substances that cause an allergy or intolerance
- Microbiology of foods
- Antimicrobial inhibitors
Antimicrobial inhibitors
The CNA's antibiotic laboratory collaborates with the corresponding European Union Reference Laboratory (ANSES)
The development of antibiotic resistant bacterial strains is a natural phenomenon that occurs when microorganisms are exposed to antimicrobial drugs. Furthermore, it may cause an exchange of resistance characteristics amongst certain types of bacterias increasing the proliferation of resistant strains. The inappropriate use of antimicrobial drugs accelerates this natural phenomenon.
The CNA has developed techniques both for the detection of residues of antimicrobial substances in foods of animal origin and techniques for the study of sensitivity or resistance of isolated microorganisms of foods.
Microbiological screening of microbial growth inhibitor residues
It has accredited microbiological methods for the carrying out of screening and post-screening in the determination of residues of antimicrobial substances included in Group B1 of veterinary drug residues and contaminants in foods of animal origin (Directive 96/23/EC):
- Residue screening technique for antibacterials with 5 plates
- Residue screening technique for antibacterials in milk due to inhibition of Bacillus stearothermophillus
- Residue post-screening technique for antibacterials by multiple bioassay
Furthermore, it has a method developed/validated for the screening of antibacterial residues in muscle due to inhibition of Bacillus stearothermophilus (Test Explorer 2.0).
It is in a position to develop/validate the analytical methodologies necessary for addressing the potential alerts that appear in this field.
Amongst the tasks typical of its position as NRL, we should mention in particular:
- The annual organisation of intercomparison exercises both for the screening technique of the 5 plates, and for the post-screening technique by multiple bioassay.
- The transfer of NRL work standardised procedures (and their validations), through the controlled distribution lists, with the aim of facilitating access to the accreditation of these tests –within the system established by Technical Note NT-55 of ENAC- of laboratories designated to carry out the official control.
Antimicrobial resistance
The CNA’s Antimicrobial Resistance laboratory collaborates with the European Union Reference Laboratory (DTU Food, Denmark).
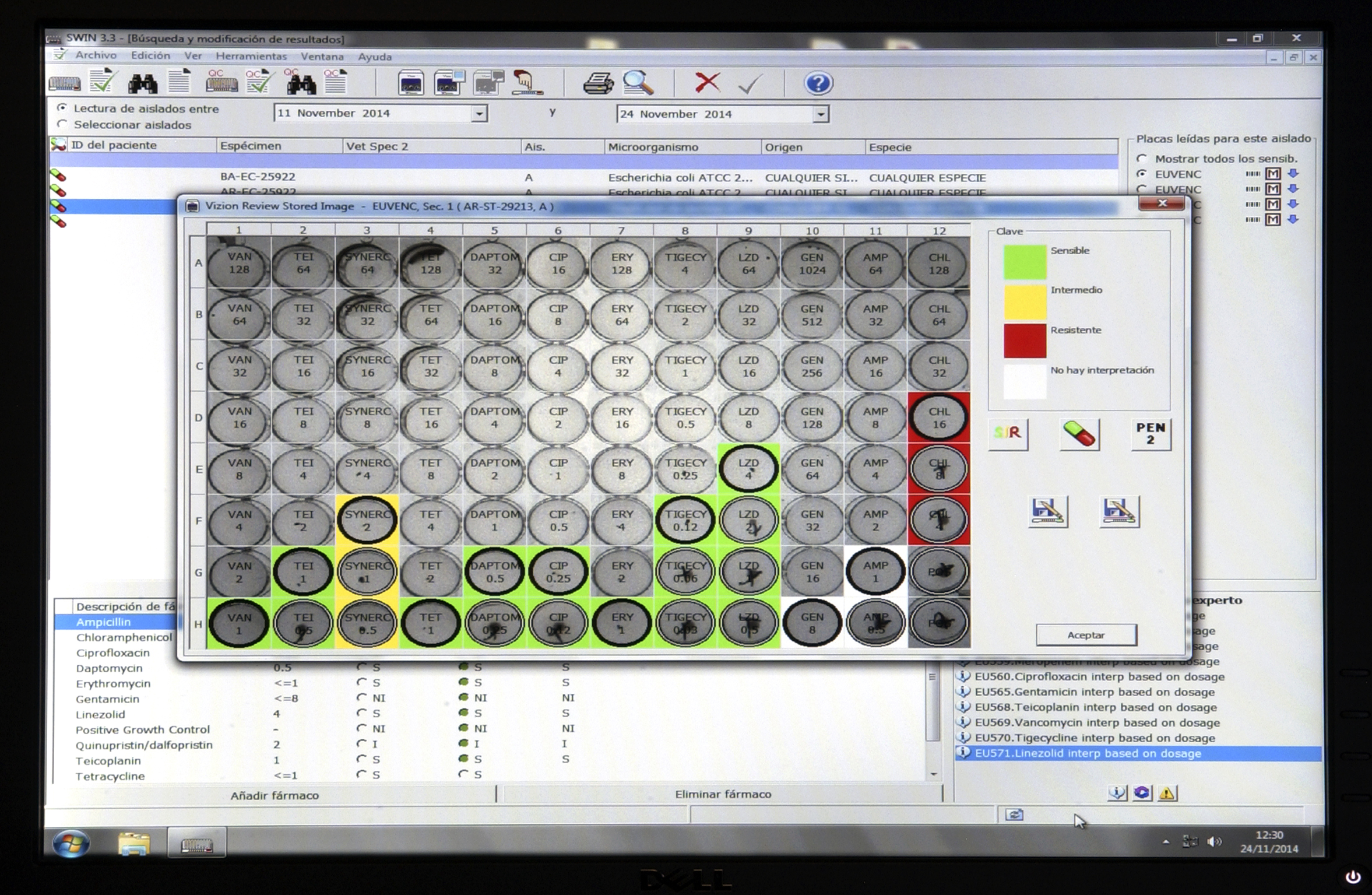
It has a quantitative method validated and developed in a standardised manner in the European Union (Decision 2013/652/EU) for the analysis of the resistance to antibiotics of enterobacteriaceae and other microorganisms isolated in foods.
Assessment of the minimum inhibitory concentration of antimicrobials against bacterial strains by microdilution.
There are various panels with a different selection of antibiotics in accordance with the type of organism studied, for gram positive or negative microorganisms or even a specific panel for the study of sensitivity to beta-lactam antibiotics.